Ataraxia: When Nothing Affects Us Emotionally

The concept of ataraxia dates back to Ancient Greece and the Stoics, and it means not being affected by situations and remaining serene in the face of adversity. This state of mind free from fear, anxiety, anger and frustration seems idyllic, after all, who wouldn’t want to live with such peace of mind?
The truth is that this reality has little to do with health or even logic. For example, João Sem Fear, a character in a tale by the Brothers Grimm, spent a good part of his life trying to get to know this emotion that so defines human beings. It is noteworthy that excluding an emotion from the emotional record, whatever it may be, can have serious consequences.
This is why ataraxia, far from being an inspiring concept, can actually be a disorder. Furthermore, it could even be a neurological disorder. This is because anguish and restlessness, although uncomfortable and even disturbing, fulfill an indisputable purpose in terms of survival.

Definition of ataraxia
Greek philosophy defined ataraxia as imperturbability. Figures such as Democritus or Heraclitus considered that this ability to reduce passion and show a serene, restrained and impenetrable behavior by emotions and instincts was synonymous with elevation and nobility of spirit.
This view of behavior and attitude was developed by the Epicureans, Stoics and Skeptics. In this regard, research by Dr. James Warren of Cambridge University indicates that Epicureans considered ataraxia synonymous with mental well-being. For them, it could “uproot” fears from the mind.
Seen from this perspective, many people may consider ataraxia as something encouraging and beneficial, after all, q ho would not want to live in a permanent state of imperturbability in a psychological sphere where nothing would affect him ?
However, the truth is that if we reacted to the adversities of life in this way, we would not be human, we would be machines. Even the inability to react to events in the environment or the absence of fear would define, in many cases, a neurological disorder.
Symptoms
Ataraxia is not in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V). However, as we mentioned earlier, it could be a symptom of a neurological problem. Several brain alterations correlate with this reality and its symptoms.
- Passive behavior and inability to react to surrounding stimuli.
- A person with medical ataraxia has no mood swings. She is always in a state of emotional emptiness in which she has neither emotional ups nor downs, joy, fear, illusions or concerns.
- She does not express frustration. In other words, she experiences the fact of making mistakes or not being able to fulfill her goals, for example, calmly and almost indifferently.
- She doesn’t feel guilty or responsible for her actions.
- Likewise, it is common that she does not respect limits or be aware of the risk of her behavior.
Clinical or medical ataraxia is the extreme form of philosophical ataraxia. In other words, one can maintain a calm and calm character in the face of life’s events. However, it is expected – and recommended – that we experience joy, guilt, fear, anguish, the outpouring of love and, at times, even the discomfort of sadness.
These emotions allow us to adapt to life’s unforeseen events, providing us with valuable learning tools. However, someone with clinical ataraxia shows an evident maladaptive passivity. This condition of fine people who are unable to respond to their social, occupational and emotional environments.
neurological origin
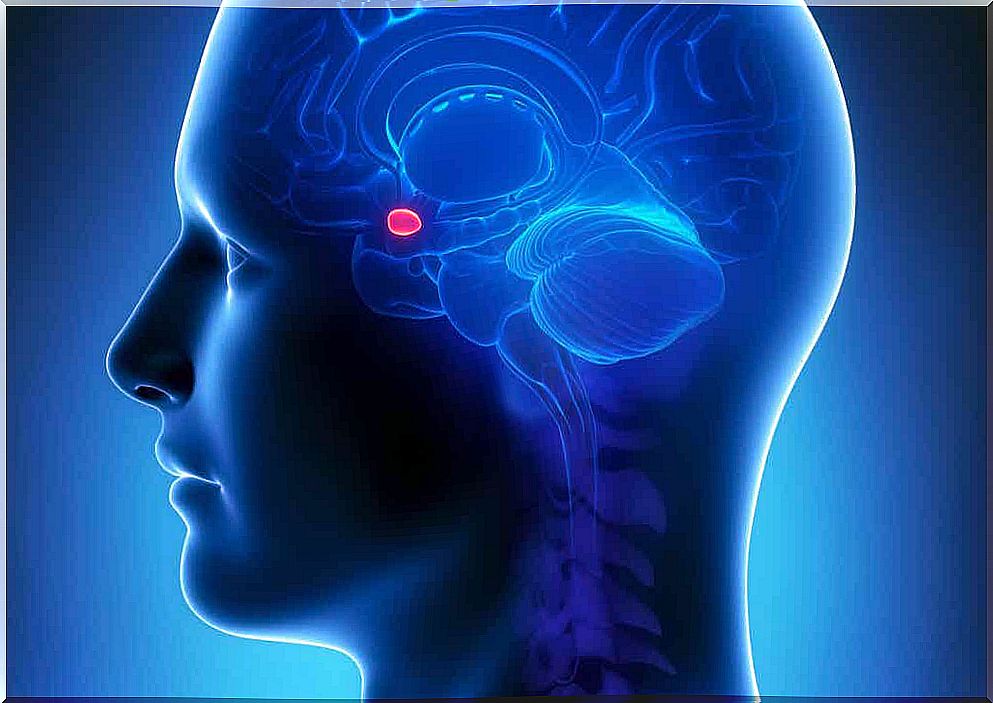
There are a few causes for ataraxia. The most common are traumatic shocks to the frontal area of the brain and strokes. In addition, it is noteworthy that the Urbach-Wiethe syndrome has as its main manifestation the total absence of fear.
This condition arises as a result of an injury or atrophy in the cerebral amygdala. This region regulates part of our emotions, with fear and alertness being the most common. Thus, when faced with danger, it is the amygdala that immediately sends information to the cerebral cortex, which will apply a cognitive filter to objectively assess the real risk.
However, a person with ataraxia is not able to carry out these processes. Thus, it is likely that Joao Fearless, from the Grimm brothers, had an alteration in his cerebral amygdala.









